Search Results
Results for: 'autoregulation via myogenic mechanism Myogenic mechanism'
Regulation of GFR: three methods, autoregulation & autoregulation via myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 11557
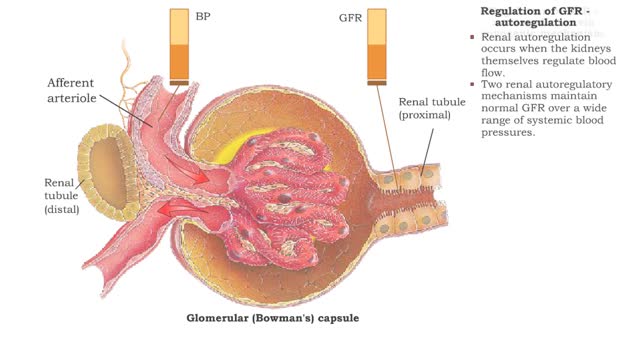
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Hormonal regulation. • Ren...
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via myogenic mechanism Myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 12590
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Renal autoregulation occurs when...
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via tubuloglomerular feedback, neural & hormonal regulation
By: HWC, Views: 12089
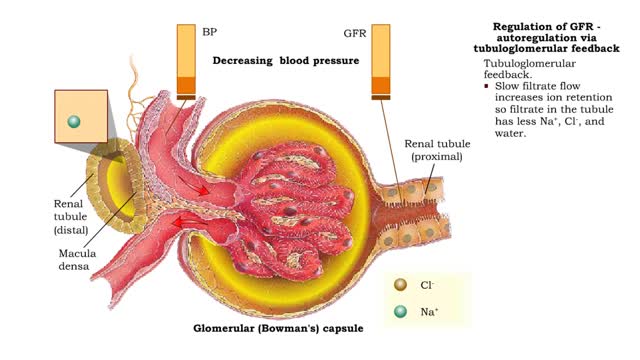
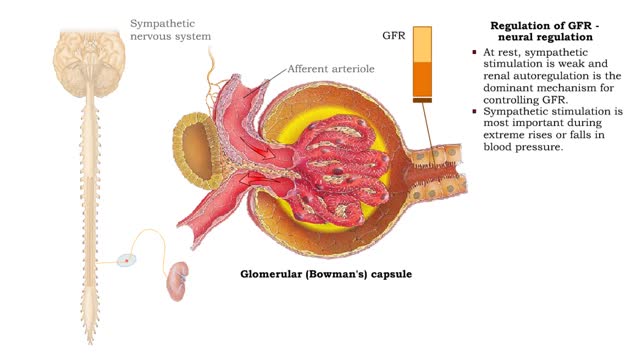
• When blood pressure is above normal, rapid filtrate flow reduces ion retention so filtrate in tubule has more Na+, C1-, and water. • It is believed that vasoconstricting chemicals from the juxtaglomerular cells are released when the macula densa cells detect higher water and ion levels in ...
By: HWC, Views: 10839
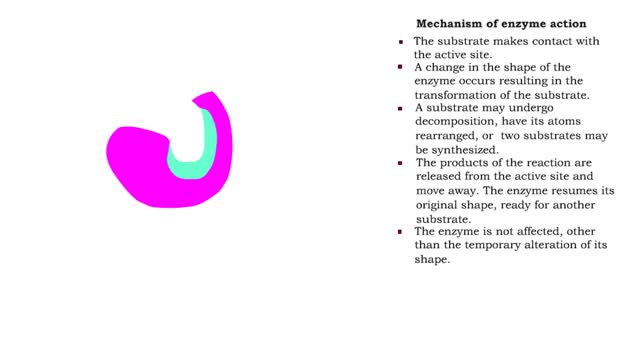
■ The substrate makes contact with the active site. ■ A change in the shape of the enzyme occurs resulting in the transformation of the substrate. ■ A substrate may undergo decomposition, have its atoms rearranged, or two substrates may be synthesized. ■ The products of the reaction...
By: Administrator, Views: 15158
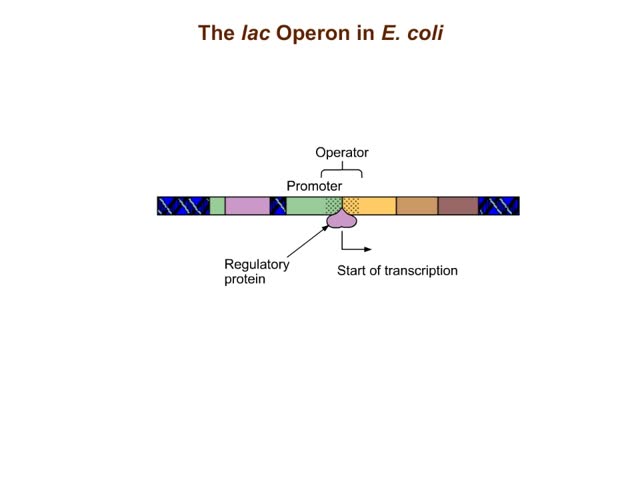
The lac operon (lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is no...
Second Stage of Labor and Delivery
By: Administrator, Views: 655
During labor forceful contractions move the fetus down the birth canal and expel it from the uterus. Signs and symptoms that labor is about to start can occur from hours to weeks before the actual onset of labor. Braxton Hicks contractions Irregular contractions that begin in the second trim...
First Stage of Labor and Delivery Video
By: Administrator, Views: 14206
During labor forceful contractions move the fetus down the birth canal and expel it from the uterus. Signs and symptoms that labor is about to start can occur from hours to weeks before the actual onset of labor. Braxton Hicks contractions Irregular contractions that begin in the second trim...
By: HWC, Views: 11807
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
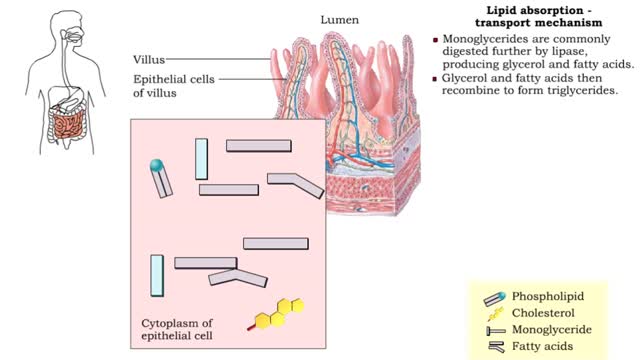
Lipid absorption - end products & transport mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 10618
• The end products, fatty acids and monoglycerides, depend on bile salts for absorption. • Bile salts form micelles (tiny spheres), which ferry fatty acids and monoglycerides to epithelial cells. • Free fatty acids, monoglycerides, and some phospholipids and cholesterol molecules, dif...
Advertisement